Introduction
An informative essay is like giving someone the 411—it’s the information. It’s like what Wikipedia and web cultivators are supposed to do (but often fail at due to some developer bias on the backend).
When you call 411 from your mobile phone, you’re not looking for the operator’s opinion, are you? “Hey, operator, what’s the address for the Korean BBQ place in Toronto?” “Oh, you don’t want that—it’s not very good—I’ll give you some nice sushi restaurants to try instead.” “No, no, I just want the address for Korean BBQ.” “I once had a bad experience with Korean BBQ, so I’d rather not tell you about that. How about I tell you about the new outfit I bought this weekend? Also, in my opinion there are better things to try.” “No, but I just want—”.
Nobody wants to live through that experience. The same goes for writing an informative essay: your professor is not looking for your opinion or some tangential line of thought—just the information relevant to the topic.
Informative essays are meant to educate the reader about something specific by presenting the appropriate facts and giving a detailed explanation. They are often assigned in high schools and colleges because they help students develop research skills and gain experience in presenting information clearly. These are real-world skills you will want to possess.
So how do you write an informative essay? Where do you start? What’s the biggest challenge?
Organization, purpose, and clarity are the big issues to tackle. And that’s where we start.
Organize the material and present it in a way that is readable. The informative essay should have a logical structure. How that logic appears depends upon the purpose. The general purpose is to inform the reader—but you need a plan for how to do this, what specifically you are going to focus on, how far down into the subject you are going to probe, and what you want the reader to be able to walk away with when it’s all said and done.
And it all needs to be written as clearly and coherently as possible. This is not the time for waxing lyrically about seeing through a glass darkly. We want the glass to be perfectly transparent and translucent—like a bottle of Windex was just used on it and the sun is filling it all up.
Informative essays are one of the oldest types of essays in existence because they get to the heart of what writing has always been about: conveying knowledge from one person to another. That’s all this style of writing does. From the ancient poets like Homer to the modern scribes of today, information is the most important resource in the whole wide world. Poets dress it up to make it more palatable and pleasing. Technical writers trim it down to make it precise for step-by-step procedurals. The informative essayist falls somewhere in between the two poles—neither poet nor industrial manual author. He is explaining something—and to start off he needs to be able to tell the reader exactly what he aims to do and how he intends to do it.
In this tutorial, we’re going to go over everything you need to know to write an amazing informative essay. Our comprehensive guide gives an overview of the step-by-step writing process you need to follow as well as a detailed outline structure that will help you organize your thoughts. We follow that up with not one but TWO informative essay examples so that you can walk away with a perfect idea of what your writing can look like.
Comprehensive Guide
Definition
An informative essay is a form of writing that teaches the reader about a specific subject. Unlike persuasive or argumentative essays, which seek to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint, an informative essay does not focus on convincing anyone of anything. It has no point of view. It is merely interested in the objective, factual information and explaining without personal opinions or persuasive techniques. The goal is to present to the reader unbiased, clear, accurate, and topically relevant information in an organized manner. We just want the reader to know about the subject. We are not trying to convince the reader to hold a particular opinion about it.
Purpose
The primary purpose of an informative essay is to inform and educate the reader. With this style of writing, students learn to gather information from reliable sources, evaluate the accuracy of that information, and present it logically and coherently. Overall, the purpose is to increase the reader’s knowledge and understanding of a subject without overtly attempting to influence or alter opinions or beliefs. It is telling the information without telling the reader what to think about it. The reader is allowed to make up his own mind based on the information received. The writer so much as says, “Here, take this information. Now, do with it what you will.”
View 120,000+ High Quality Essay Examples
Learn-by-example to improve your academic writing
Key Differences
Informative essays differ significantly from persuasive and argumentative essays in terms of objectivity vs. subjectivity, structure, and tone.
- Objective vs. Subjective
- Informative Essay: Focuses on factual information and explanations. It is objective and neutral, presenting no specific side or point of view.
- Persuasive Essay: Seeks to convince the reader to adopt a viewpoint (for example, pro or con). Even though it may include objective facts, it is necessarily subjective in presentation and often includes emotional appeals.
- Argumentative Essay: Similar to a persuasive essay but relies more on logical reasoning and evidence to support a specific argument. It presents multiple sides of an issue but argues in favor of one. Relies more on data than on emotion to make a case.
- Structure
- Informative Essay: Typically follows a straightforward structure with an introduction, body paragraphs that present information logically, and a conclusion. Each section serves to inform rather than persuade.
- Persuasive Essay: Includes an introduction with a strong thesis statement, body paragraphs that present points or may use different methods of persuasion (anecdotes, personal appeals, facts, etc.), and a conclusion that reinforces the writer’s position.
- Argumentative Essay: Features an introduction with a clear thesis, body paragraphs that present evidence and counter-evidence, arguments and counter-arguments, and a conclusion that emphasizes the overall argument’s validity once all things are considered.
- Tone
- Informative Essay: Maintains a neutral and impartial tone. The language is formal and straightforward, focusing on clarity and accuracy, and is not given to hyperbole and exaggeration, emotion or pathos.
- Persuasive Essay: Often employs a more passionate and convincing tone. The language may be emotive and rhetorical.
- Argumentative Essay: Uses a balanced tone, combining logical reasoning with evidence. The language is formal but may include strong assertions and rhetoric to support the argument, which nonetheless must be grounded in observable facts and reason.
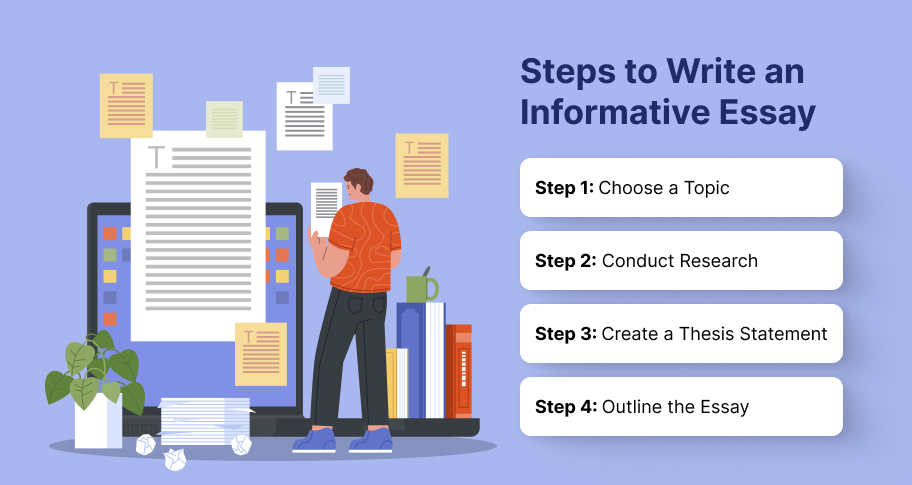
Step-by-Step to Writing an Informative Essay
Choosing a Topic
The first step is to pick a topic that you can describe or explain or want to learn more about. Choose a subject that interests you and has sufficient information available. Make sure the topic is neither too broad nor too narrow. A well-defined topic (something like: What started the Cold War and how did it end?) allows for a focused and detailed exploration, and helps your essay to be informative and engaging.
Research
Thorough research is vital to informative essay writing. Sources such as academic journals, books, reputable websites, and expert interviews can all be used to gather information. Along the way, try to verify facts by cross-referencing sources. That’s what research is all about. Be sure to cite all your information to protect yourself from plagiarism, and give a reference list of the sources used at the end of your paper. This shows where you got your information from and gives readers an idea of where they can look if they want to know more about the topic.
Thesis Statement Creation
A strong thesis statement will guide your informative essay. It should clearly articulate the main point or focus of your essay. To write a thesis statement, first, identify the core message you want to communicate and make sure it is specific. For example, instead of saying, “Climate change affects ecosystems,” specify one ecosystem in particular and focus on that: “Climate change substantially impacts coastal ecosystems by altering habitats, increasing erosion, affecting marine life, and harming the human population as well.” This statement presents a clear, specific focus and lists all the points or sub-topics you will cover in your essay; it’s perfect.
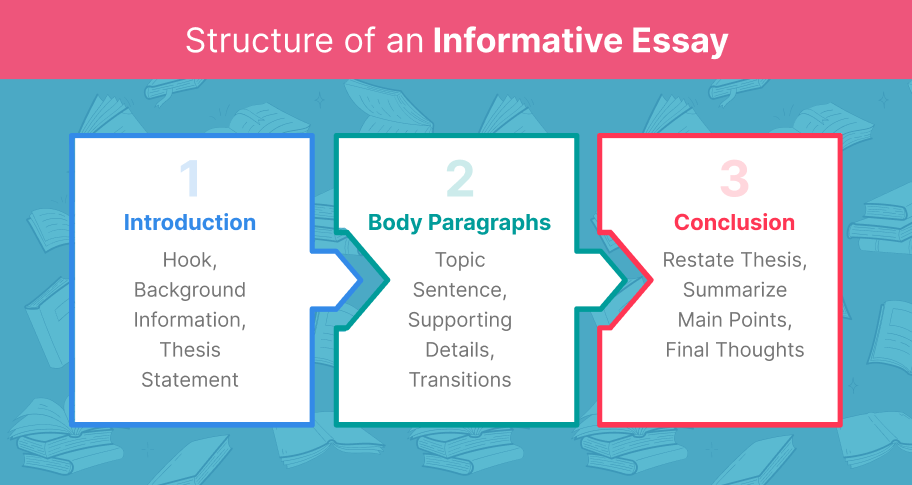
Detailed Outline Structure
Introduction
Hook
Use a hook to grab the reader’s attention—something interesting, provocative, and relevant. For example, “Did you know that the world’s oceans absorb about 30% of the carbon dioxide produced by human activities?” This factoid helps nab the reader while introducing the topic of the essay.
Background Information
Next, provide some background information. Context helps bring the reader up to speed quickly and efficiently. A broad overview of the subject, its significance, and why it matters in a few sentences is sufficient.
Thesis Statement
Conclude the intro with the thesis statement, which should bring the essay into tight focus. For example, “This essay explains the impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems by detailing its effects on habitats, erosion, marine life, and the human population.”
Body Paragraphs
Topic Sentence
Each body paragraph should begin with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. For example, “One major impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems is habitat loss.”
Supporting Details
After the topic sentence, supporting details should follow. This could include data, examples, statistics, and explanations. For example, you might describe how rising sea levels erode coastal habitats and how that negatively impacts both wildlife and human communities.
Transitions
Use transitions between paragraphs for a smooth flow of ideas. Phrases like “furthermore,” “in addition,” and “on the other hand” help connect the train of thought. For example, “In addition to habitat loss, climate change also reduces the abundant diversity of marine life, upsetting the balance of the ecosystem.”
Conclusion
Restate Thesis
The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis but in different words. For example, “In summation, climate change negatively affects coastal ecosystems by altering habitats, accelerating erosion, reducing marine life, and imperiling human life.”
Summarize Main Points
Briefly summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs by referencing a few of the more important details—just a few sentences will suffice.
Final Thoughts
End with a final thought—something to impress upon the reader. This could be a call to action, a thought-provoking question, or a suggestion for further research. For example, “Addressing the impacts of climate change on coastal ecosystems requires urgent action and collaboration among global communities. What steps can we take to protect these vital environments for future generations?”
Informative Essay Examples
Informative Essay Example 1
Impact of Climate Change on Coastal Ecosystems
Coastal ecosystems are extremely vulnerable to the effects of climate change. You might not know it, but these ecosystems include beaches, estuaries, mangroves, and coral reefs, all of which act as habitats for many different species. These ecosystems also support the livelihoods of millions of people all over the world. For these reasons, they are very important to animal and human life and any change that affects them should be understood. This essay, therefore, explains how climate change impacts coastal ecosystems, by altering habitats, increasing erosion, depleting marine life, and disrupting the human population.
One of the most substantial impacts of climate change on coastal ecosystems is habitat alteration (Chapman et al., 2020). As the temperature of the planet increases, polar ice caps melt and sea levels rise. The rise in sea level can totally submerge or wipe away coastal habitats such as marshes, mangroves, and beaches. All the species that live there are pushed out. This includes birds, fish, and invertebrates that go to these areas for breeding, feeding, nesting, or seeking shelter. For example, mangrove forests are also nurseries for many marine species. However, as these forests decline, the species that depend on them are put into jeopardy.
Coastal erosion in particular is a major impact of climate change on beaches and barrier reefs (Masselink et al., 2020). Coastal erosion can cause property loss, disrupt local economies that depend on tourism and fishing, and take away natural buffers against storm surges. As more and more natural defenses erode, coastal communities and habitats become more and more vulnerable to flooding and storm damage (Masselink et al., 2020).
In addition to habitat change and coastal erosion, climate change also reduces marine life within coastal ecosystems. Ocean acidification is one harmful outcome of increased carbon dioxide absorption by seawater (Findlay & Turley, 2021). Marine life with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons, such as corals, mollusks, and some plankton species, are all damaged as a result. For example, coral bleaching weakens coral reefs to the point that they can no longer support marine biodiversity. This in turn disrupts the entire marine food web, and everything from tiny plankton to large fish species to the people who rely on their abundance is harmed.
In conclusion, climate change is bad news for coastal ecosystems. Habitat loss due to rising sea levels, coastal erosion, and changes in marine life all represent the danger. Some consideration of what can be done at the human level to address this danger is needed. If we want to preserve the biodiversity of the earth, we need to look at what climate change is doing to our beaches.
References

Informative Essay Example 2
Benefits of a Healthy Diet
A healthy diet is an important part of a healthy lifestyle. Diet is where people draw all their energy from—the foods and liquids they consume represent the source of nutrients the body needs to stay resilient. This essay explains the benefits of a healthy diet by describing how a good diet can boost physical health, improve mental health, and prevent illnesses like diabetes and heart disease.
One of the biggest benefits of a healthy diet is the fact that it is good for one’s physical health (Zavitsanou & Drigas, 2021). A balanced diet consists of protein, fruit, veggies, whole grains, and healthy fats. That should give the body all it needs in terms of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. For example, calcium and vitamin D are needed for bone health; iron is needed for oxygen transport in the blood; and nutrient-dense foods help the body to repair tissues and keep energy up. In contrast, a diet loaded up on sugars and consisting of a lot of pre-packaged food can be a total drag on one’s energy and resilience and can open the door to poor physical and mental health. But a healthy diet can help one stay fit and prevent obesity-related health problems (Zayitsanou & Drigas, 2021).
A good diet also affects mental health in a big way. For example, omega-3 fatty acids found in fish support brain health and can reduce feelings of depression. Antioxidants from fruits and vegetables can protect brain cells from oxidative stress associated with cognitive decline. A healthy diet can even improve one’s sleep quality, which is important in terms of reducing one’s mental stress and fatigue.
A healthy diet can even prevent the onset of some diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. A diet high in processed foods and added sugars tends to be most commonly associated with the aforementioned diseases. On the other hand, a diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and healthy fats tends to be associated with the prevention of these diseases. For example, the Mediterranean diet has been linked by researchers to a lower risk of heart disease and stroke (Cai et al., 2024).
Overall, a healthy diet offers numerous benefits that can improve one’s health. It supports physical health by giving the body the nutrients and energy it needs. It helps the mind by helping the body. And it prevents the onset of burdensome diseases. That is why it is helpful for people to have healthy eating habits from an early age.
References

Conclusion
Informative essays are great ways to teach people about specific subjects. They need to be well-organized, full of factual and well-sourced information, and clearly written with a logical structure. Writing this type of essay can teach you how to research and present your findings in a coherent manner. Informative essays help refine your writing and communicating skills, which are so much in demand in the real-world.
In this article, we explained the definition and purpose of informative essays. We described their objective nature vs. persuasive and argumentative essays. We discussed their importance in academic settings. We outlined the step-by-step writing process, and we gave a detailed outline structure with examples of informative essays you can use to see how it’s done.
We encourage our readers to use the provided examples and templates to write your own informative essay outline.
For further assistance, try out our other writing tools: Hypothesis Generator, Thesis Statement Generator, and Outline Generator.
Leave a comment below and, if you found this tutorial helpful, share with friends and family!





